RGS1
| edit |
| Regulator G-proteinske signalizacije 1 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB prikaz baziran na 2bv1. | |||||||||||
| Dostupne strukture | |||||||||||
| 2BV1, 2GTP | |||||||||||
| Identifikatori | |||||||||||
| Simboli | RGS1; 1R20; BL34; HEL-S-87; IER1; IR20 | ||||||||||
| Vanjski ID | OMIM: 600323 MGI: 1354694 HomoloGene: 2191 GeneCards: RGS1 Gene | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Pregled RNK izražavanja | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
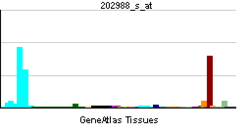 | |||||||||||
| podaci | |||||||||||
| Ortolozi | |||||||||||
| Vrsta | Čovek | Miš | |||||||||
| Entrez | 5996 | 50778 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000090104 | ENSMUSG00000026358 | |||||||||
| UniProt | Q08116 | Q9JL25 | |||||||||
| Ref. Sekv. (iRNK) | NM_002922 | NM_015811 | |||||||||
| Ref. Sekv. (protein) | NP_002913 | NP_056626 | |||||||||
| Lokacija (UCSC) | Chr 1: 192.54 - 192.55 Mb | Chr 1: 144.24 - 144.25 Mb | |||||||||
| PubMed pretraga | [1] | [2] | |||||||||
Regulator G-proteinske signalizacije 1 je protein koji je kod ljudi kodiran RGS1 genom.[1][2][3]
Ovaj gen kodira člana familje regulatora G-proteinske signalizacije. Ovaj protein je lociran na citosolnoj strani ćelijske membrane i sadrži konzervirani, 120 aminokiselina dug motiv koji se naziva RGS domen. On umanjuje signalnu aktivnost G-proteina putem vezivanja za aktivirane, GTP-vezane G alfa podjedinice, i tako što deluje kao GTPazni aktivirajući protein (GAP), povećanjem brzine konverzije GTP do GDP. Ova hidroliza omogućava alfa podjedinicama da se vežu za G beta/gama heterodimerne podjedinice, formiraju neaktivne G-proteinske heterotrimere, i time prekinu signal.[3]
Reference
- ↑ Newton JS, Deed RW, Mitchell EL, Murphy JJ, Norton JD (Jan 1994). „A B cell specific immediate early human gene is located on chromosome band 1q31 and encodes an alpha helical basic phosphoprotein”. Biochim Biophys Acta 1216 (2): 314–6. DOI:10.1016/0167-4781(93)90163-8. PMID 8241276.
- ↑ Druey KM, Blumer KJ, Kang VH, Kehrl JH (May 1996). „Inhibition of G-protein-mediated MAP kinase activation by a new mammalian gene family”. Nature 379 (6567): 742–6. DOI:10.1038/379742a0. PMID 8602223.
- ↑ 3,0 3,1 „Entrez Gene: RGS1 regulator of G-protein signalling 1”.
Literatura
- Hong JX, Wilson GL, Fox CH, Kehrl JH (1993). „Isolation and characterization of a novel B cell activation gene.”. J. Immunol. 150 (9): 3895–904. PMID 8473738.
- Heximer SP, Cristillo AD, Forsdyke DR (1997). „Comparison of mRNA expression of two regulators of G-protein signaling, RGS1/BL34/1R20 and RGS2/G0S8, in cultured human blood mononuclear cells.”. DNA Cell Biol. 16 (5): 589–98. DOI:10.1089/dna.1997.16.589. PMID 9174164.
- Bowman EP, Campbell JJ, Druey KM, et al. (1998). „Regulation of chemotactic and proadhesive responses to chemoattractant receptors by RGS (regulator of G-protein signaling) family members.”. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (43): 28040–8. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.43.28040. PMID 9774420.
- Denecke B, Meyerdierks A, Böttger EC (1999). „RGS1 is expressed in monocytes and acts as a GTPase-activating protein for G-protein-coupled chemoattractant receptors.”. J. Biol. Chem. 274 (38): 26860–8. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.38.26860. PMID 10480894.
- Popov SG, Krishna UM, Falck JR, Wilkie TM (2000). „Ca2+/Calmodulin reverses phosphatidylinositol 3,4, 5-trisphosphate-dependent inhibition of regulators of G protein-signaling GTPase-activating protein activity.”. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (25): 18962–8. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M001128200. PMID 10747990.
- Zheng B, Chen D, Farquhar MG (2000). „MIR16, a putative membrane glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase, interacts with RGS16”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (8): 3999–4004. DOI:10.1073/pnas.97.8.3999. PMC 18131. PMID 10760272.
- Lou X, Yano H, Lee F, et al. (2001). „GIPC and GAIP Form a Complex with TrkA: A Putative Link between G Protein and Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Pathways”. Mol. Biol. Cell 12 (3): 615–27. DOI:10.1091/mbc.12.3.615. PMC 30968. PMID 11251075.
- Hoffmann M, Ward RJ, Cavalli A, et al. (2001). „Differential capacities of the RGS1, RGS16 and RGS-GAIP regulators of G protein signaling to enhance alpha2A-adrenoreceptor agonist-stimulated GTPase activity of G(o1)alpha”. J. Neurochem. 78 (4): 797–806. DOI:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00479.x. PMID 11520900.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). „Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. DOI:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). „Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs”. Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. DOI:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). „The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)”. Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. DOI:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Le Y, Honczarenko M, Glodek AM, et al. (2005). „CXC chemokine ligand 12-induced focal adhesion kinase activation and segregation into membrane domains is modulated by regulator of G protein signaling 1 in pro-B cells”. J. Immunol. 174 (5): 2582–90. DOI:10.4049/jimmunol.174.5.2582. PMID 15728464.
- Han JI, Huang NN, Kim DU, Kehrl JH (2006). „RGS1 and RGS13 mRNA silencing in a human B lymphoma line enhances responsiveness to chemoattractants and impairs desensitization”. J. Leukoc. Biol. 79 (6): 1357–68. DOI:10.1189/jlb.1105693. PMID 16565322.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE, et al. (2006). „The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1”. Nature 441 (7091): 315–21. DOI:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
- p
- r
- u
PDB Galerija
|