Dirakova delta funkcija

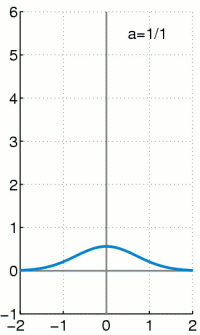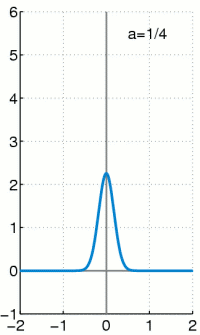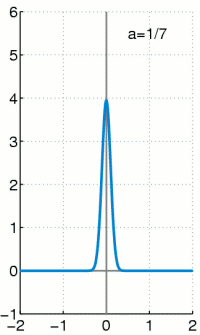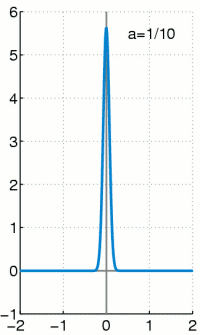
Dirakova (delta) funkcija ili δ funkcija se opisuje kao funkcija u realnoj ravni, čija je vrednost u svim tačkama 0, osim u tački 0 kada iznosi beskonačno mnogo, definisana tako da je njen integral po celoj oblasti definsanosti 1.
δ funkciju je formulisao teoretski fizičar Pol Dirak. Diskretna analogija Dirakove funkcije je Kroneker delta funkcija, koja je obično definisana u konačnom domenu i uzima vrednosti između 0 i 1.
Iako gledano iz čisto matematičke strane, Dirakova delta funkcija nije striktna funkcija, odnosno nije funkcija u pravom smislu tih reči. Integral bilo koje realne funkcije koja doseže do beskonačnosti i ima vrednost u svim tačkama 0, a samo u jednoj tački vrednost 1 imao bi vrednost 0, a ne 1 što je slučaj sa δ funkcijom. Dirakova delta funkcija ima smisao jedino kada se pojavljuje kao matematički objekat unutar integrala. Formalno se mora definisati kao distribucija ili mera. U mnogim primenama, δ funkcija predstavlja graničnu vrednost niza funkcija normalnih distribucija sa tačkom nagomilavanja u nuli, iako su približne vrednosti ovih raspodela samo približna vrednost δ funkcije.
Definicija
Dirakova delta funkcija je najpribližnije rečeno funkcija na realnoj pravoj čija je vrednost svugde nula, osim u koordinatnom početku. gde je njena vrednost beskonačna,
i defisana da zadovoljava identitet da je njen integral u intervalu od do jednak 1,
δ funkcija se formalno definiše kao distribucija ili mera.
Sličnost sa Kronekerovom delta funkcijom
Kronekerova delta funkcija se za cele brojeve i i j definiše kao:
Tada za sve nizove koji su beskonačni u oba pravca (dosežu i do i do ), važi:
Slično, za bilo koju realnu ili kompleksnu funkciju ƒ neprekidnu u R, Dirakova delta funkcija zadovoljava osobinu:
Povezanost osobina ovih dveju funkcija čini Kronekerovu delta funkciju diskretnom analogijom Dirakove delta funkcije na skupu .
Primena
δ funkcija u fizici predstavlja idealizovani centar mase. Dirakova delta distribucija se koristi u teoriji verovatnoće za diskretnu raspodelu. Diskretizovana δ funkcija je ključna za formulisanje ortonormalnosti u kvantnoj mehanici. Koristi se i u teoriji konstrukcija za opisivanje prolaznog opterećenja ili tačke opterećenja u strukturama.
Vidi još
Literatura
- Aratyn, Henrik; Rasinariu, Constantin (2006). A short course in mathematical methods with Maple. World Scientific. ISBN 981-256-461-6. .
- Arfken, G. B.; Weber, H. J. (2000). Mathematical Methods for Physicists (5th изд.). Boston, MA: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-059825-0. .
- Bracewell, R. (1986), The Fourier Transform and Its Applications (2nd изд.), McGraw-Hill .
- Córdoba, A., „La formule sommatoire de Poisson”, C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris, Series I, 306: 373—376 .
- Courant, Richard; Hilbert, David (1962), Methods of Mathematical Physics, Volume II, Wiley-Interscience .
- Davis, Howard Ted; Thomson, Kendall T (2000). Linear algebra and linear operators in engineering with applications in Mathematica. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-206349-X.
- Dieudonné, Jean (1976). Treatise on analysis. Vol. II. New York: Academic Press [Harcourt Brace Jovanovich Publishers]. ISBN 978-0-12-215502-4. MR 0530406. .
- Dieudonné, Jean (1972), Treatise on analysis. Vol. III, Boston, MA: Academic Press, MR 0350769
- Dirac, Paul (1958). Principles of quantum mechanics (4th изд.). Oxford at the Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-852011-5. .
- Driggers, Ronald G. (2003). Encyclopedia of Optical Engineering. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8247-0940-2. .
- Federer, Herbert (1969). Geometric measure theory. Die Grundlehren der mathematischen Wissenschaften. 153. New York: Springer-Verlag. стр. xiv+676. ISBN 978-3-540-60656-7. MR 0257325. .
- Gel'fand, I.M.; Shilov, G.E. (1966—1968), Generalized functions, 1—5, Academic Press .
- Hartman, William M. (1997). Signals, sound, and sensation. Springer. ISBN 978-1-56396-283-7. .
- Hewitt, E; Stromberg, K (1963), Real and abstract analysis, Springer-Verlag .
- Hörmander, L. (1983). The analysis of linear partial differential operators I. Grundl. Math. Wissenschaft. 256. Springer. ISBN 3-540-12104-8. MR 0717035. .
- Isham, C. J. (1995). Lectures on quantum theory: mathematical and structural foundations. Imperial College Press. ISBN 978-81-7764-190-5. .
- John, Fritz (1955), Plane waves and spherical means applied to partial differential equations, Interscience Publishers, New York-London, MR 0075429 .
- Lang, Serge (1997). Undergraduate analysis. Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics (2nd изд.). Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-94841-6. MR 1476913. .
- Laugwitz, D. (1989), „Definite values of infinite sums: aspects of the foundations of infinitesimal analysis around 1820”, Arch. Hist. Exact Sci., 39 (3): 195—245, doi:10.1007/BF00329867 .
- Levin, Frank S. (2002). „Coordinate-space wave functions and completeness”. An introduction to quantum theory. Cambridge University Press. стр. 109ff. ISBN 0-521-59841-9.
- Li, Y. T.; Wong, R. (2008), „Integral and series representations of the Dirac delta function”, Commun. Pure Appl. Anal., 7 (2): 229—247, MR 2373214, doi:10.3934/cpaa.2008.7.229 .
- de la Madrid, R.; Bohm, A.; Gadella, M. (2002), „Rigged Hilbert Space Treatment of Continuous Spectrum”, Fortschr. Phys., 50 (2): 185—216, Bibcode:2002ForPh..50..185D, arXiv:quant-ph/0109154
 , doi:10.1002/1521-3978(200203)50:2<185::AID-PROP185>3.0.CO;2-S .
, doi:10.1002/1521-3978(200203)50:2<185::AID-PROP185>3.0.CO;2-S . - McMahon, D. (2005). „An Introduction to State Space”. Quantum Mechanics Demystified, A Self-Teaching Guide. Demystified Series. New York: McGraw-Hill. стр. 108. ISBN 0-07-145546-9. doi:10.1036/0071455469. Архивирано из оригинала 26. 03. 2016. г. Приступљено 17. 3. 2008. .
- van der Pol, Balth.; Bremmer, H. (1987). Operational calculus (3rd изд.). New York: Chelsea Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-8284-0327-6. MR 904873. .
- Rudin, W. (1991). Functional Analysis (2nd изд.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-054236-8. .
- Soares, Manuel; Vallée, Olivier (2004), Airy functions and applications to physics, London: Imperial College Press .
- Saichev, A I; Woyczyński, Wojbor Andrzej (1997). „Chapter1: Basic definitions and operations”. Distributions in the Physical and Engineering Sciences: Distributional and fractal calculus, integral transforms, and wavelets. Birkhäuser. ISBN 0-8176-3924-1.
- Schwartz, L. (1950), Théorie des distributions, 1, Hermann .
- Schwartz, L. (1951), Théorie des distributions, 2, Hermann .
- Stein, Elias; Weiss, Guido (1971). Introduction to Fourier Analysis on Euclidean Spaces. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-08078-X. .
- Strichartz, R. (1994). A Guide to Distribution Theory and Fourier Transforms. CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-8273-4. .
- Vladimirov, V. S. (1971). Equations of mathematical physics. Marcel Dekker. ISBN 0-8247-1713-9. .
- Yamashita, H. (2006), „Pointwise analysis of scalar fields: A nonstandard approach”, Journal of Mathematical Physics, 47 (9): 092301, Bibcode:2006JMP....47i2301Y, doi:10.1063/1.2339017
- Yamashita, H. (2007), „Comment on "Pointwise analysis of scalar fields: A nonstandard approach" [J. Math. Phys. 47, 092301 (2006)]”, Journal of Mathematical Physics, 48 (8): 084101, Bibcode:2007JMP....48h4101Y, doi:10.1063/1.2771422
Spoljašnje veze
- Hazewinkel Michiel, ур. (2001). „Delta-function”. Encyclopaedia of Mathematics. Springer. ISBN 978-1556080104.
- KhanAcademy.org video lesson
- The Dirac Delta function, a tutorial on the Dirac delta function.









![{\displaystyle [0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/738f7d23bb2d9642bab520020873cccbef49768d)









